
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is one of the most respected indicators in professional trading environments. Widely used by institutional traders, execution desks, and algorithmic strategies, VWAP serves as a benchmark for fair value and intraday market sentiment.
For intermediate traders, VWAP is far more than a basic technical indicator. When applied correctly, it becomes a framework for understanding intraday market structure, identifying high-probability trading zones, and improving execution quality.
What is VWAP?
VWAP is the average price of security, weighted by trading volume, over a specific period—usually a single trading day. Unlike a simple moving average, VWAP considers both price and volume, offering a more accurate reflection of market activity.
Formula:
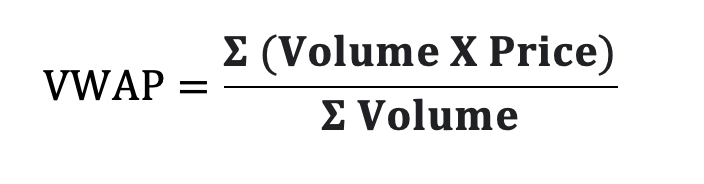
Because VWAP is recalculated continuously and resets at the start of each trading session, it is primarily used for intraday analysis rather than swing or long-term trading.
Where:
- Price = Price at each transaction
- Volume = Volume at each transaction
In simple terms:
- When price is above VWAP, buyers are in control and the market is trading at a premium.
- When price is below VWAP, sellers dominate and the market is trading at a discount.
This makes VWAP a widely accepted reference point for intraday “fair value”.
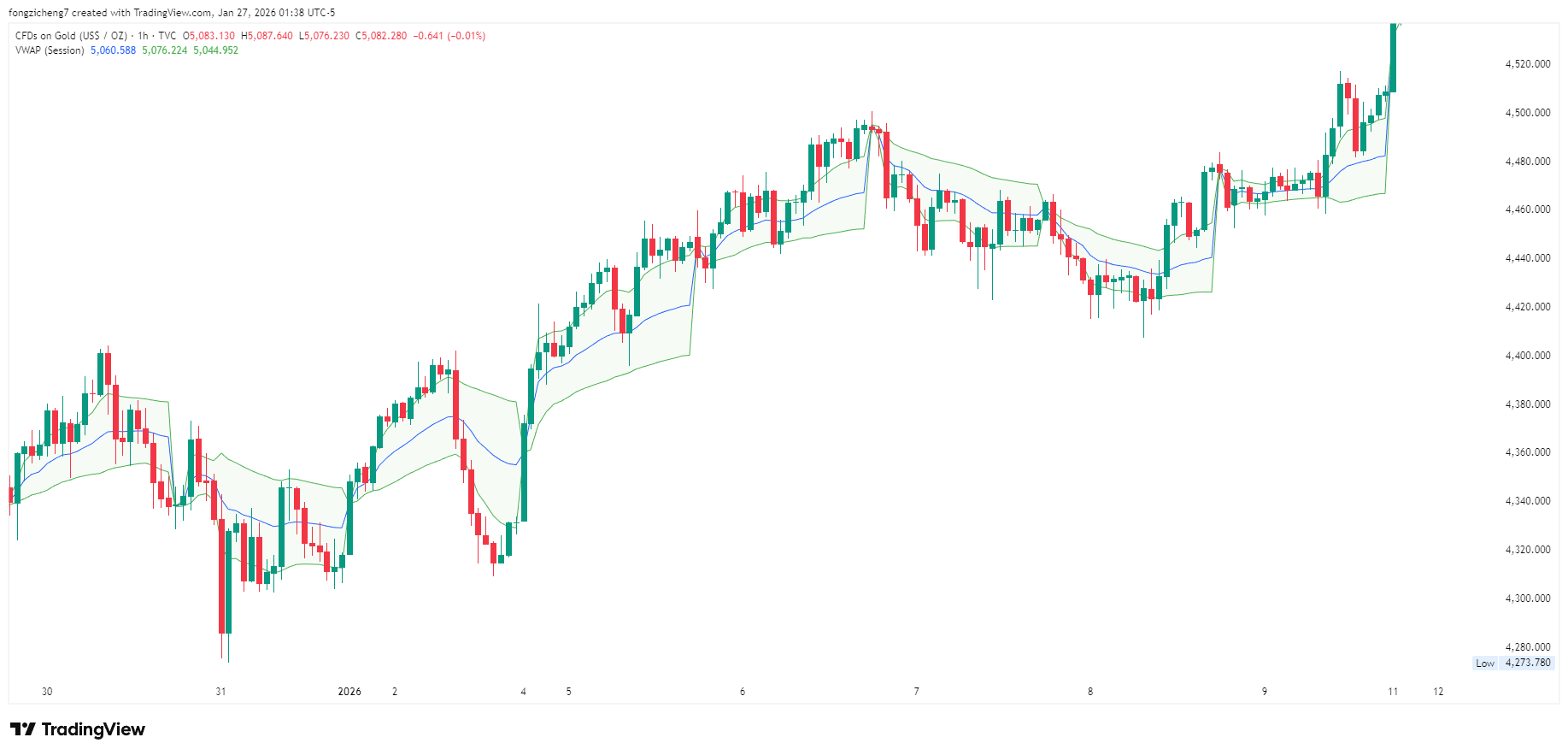
Why VWAP is Closely Watched by Institutions
Institutional traders often use VWAP as a performance benchmark. Large orders are typically executed in a way that aims to achieve an average price close to, or better than, VWAP in order to minimise market impact.
Because of this:
- Price often reacts around VWAP due to large resting orders
- VWAP frequently acts as dynamic support or resistance
- Strong moves away from VWAP can indicate aggressive institutional participation
For retail traders, understanding this behaviour provides valuable insight into where professional interest may be concentrated.
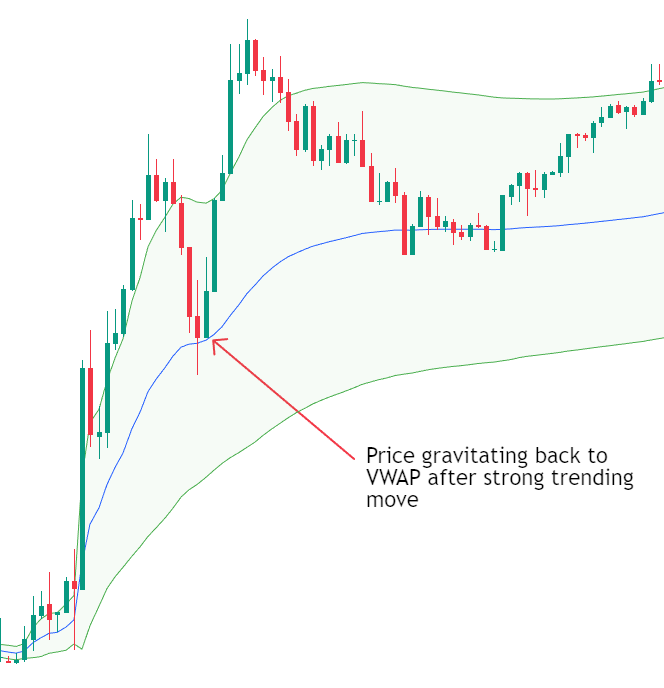
VWAP and Intraday Market Structure
VWAP plays a key role in defining intraday market structure. Markets tend to rotate around VWAP during balanced conditions and trend away from it during directional sessions.
There are generally three common intraday scenarios:
- Trending Session Price opens above VWAP and remains above it throughout the session, using VWAP as support. Pullbacks towards VWAP often attract buyers.
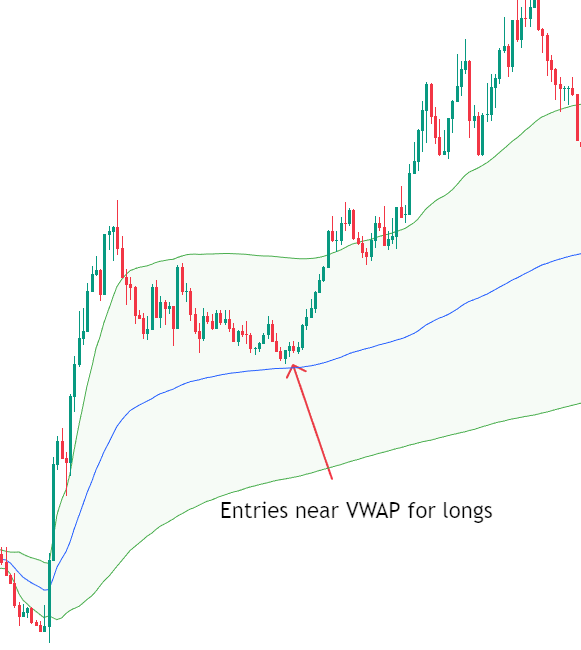
- Bearish Trending Session Price opens below VWAP and remains below it, with VWAP acting as resistance. Rallies towards VWAP are often sold.
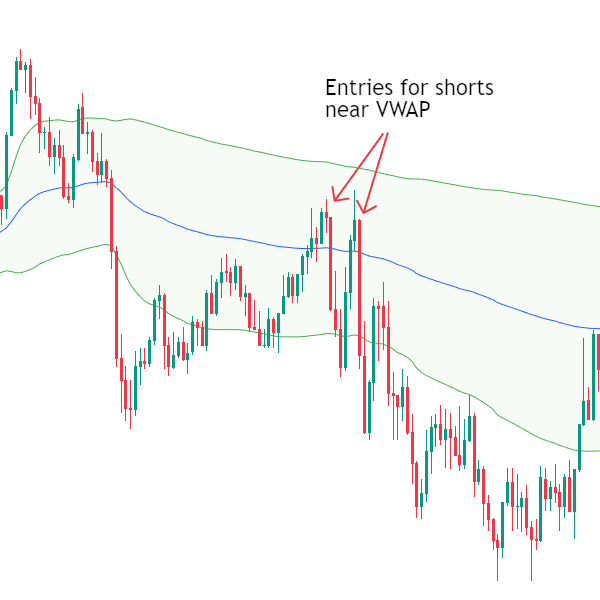
- Range-Bound Session Price repeatedly crosses VWAP, indicating a lack of clear directional conviction. Mean-reversion strategies tend to perform better in these conditions.
Recognising which environment you are trading in is critical when using VWAP effectively.
VWAP vs Other Averages
VWAP is often compared to moving averages such as SMA or EMA, but key differences make it unique:
| Feature | VWAP | SMA | EMA |
| Time weighting | Intra-day | Closing prices | Recent prices |
| Volume consideration | Yes | No | No |
| Reset frequency | Daily | Continuous | Continuous |
VWAP is particularly useful for intraday trading because it resets daily and reacts to both price and volume, reflecting market sentiment more accurately than a simple moving average.
Session Timing and VWAP Behaviour
| Trading Session | Typical VWAP Behaviour |
| Asian Session | Often range-bound, with price oscillating around VWAP due to lower liquidity. |
| London Session | Frequently introduces directional moves that establish the day’s bias relative to VWAP. |
| New York Session | May extend the existing trend or trigger sharp reversals, particularly around major economic data releases. |
Understanding session dynamics helps traders interpret VWAP more accurately and adapt their strategies to changing market conditions.
How Traders Use VWAP
a) Trend Confirmation
- Prices above VWAP indicate bullish sentiment.
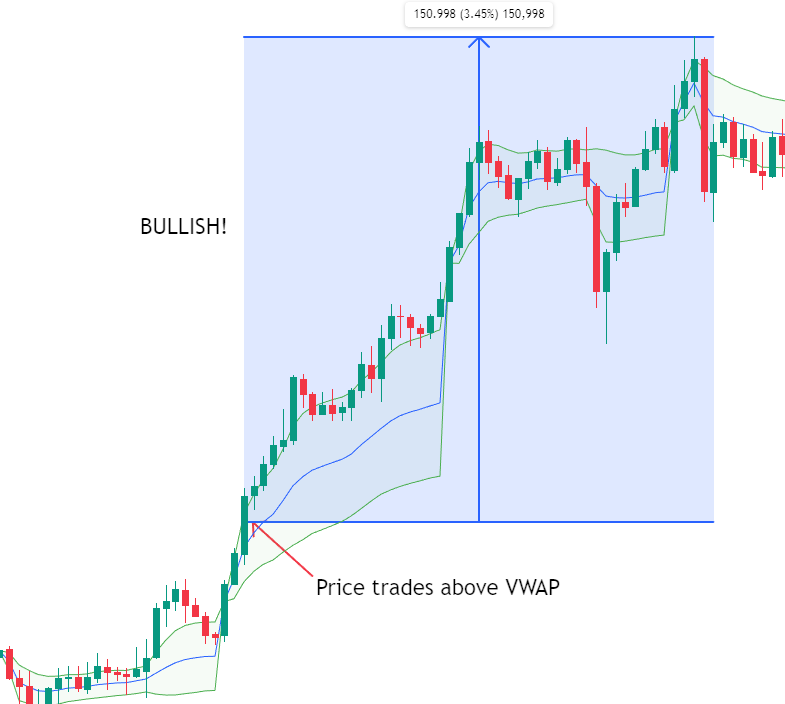
- Prices below VWAP indicate bearish sentiment.
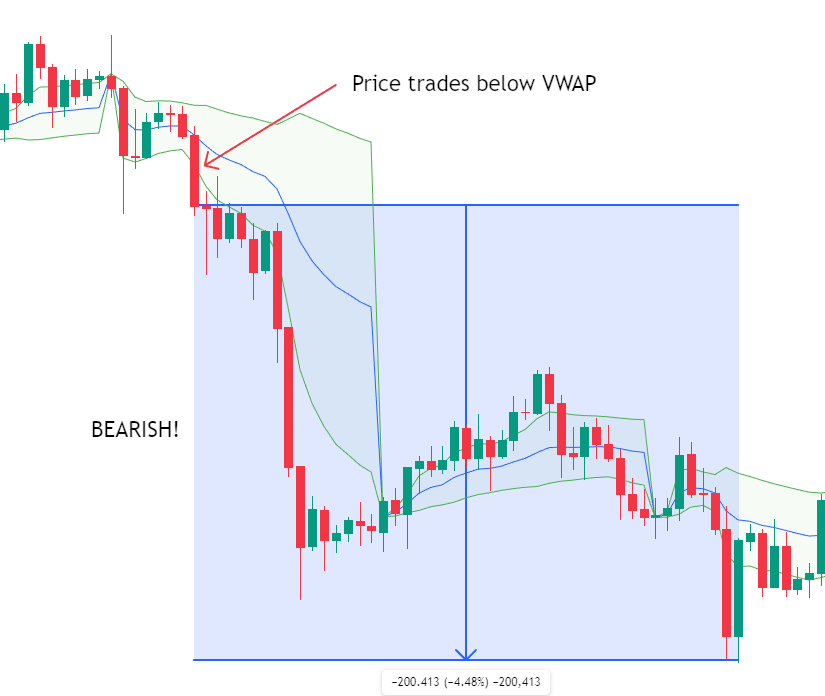
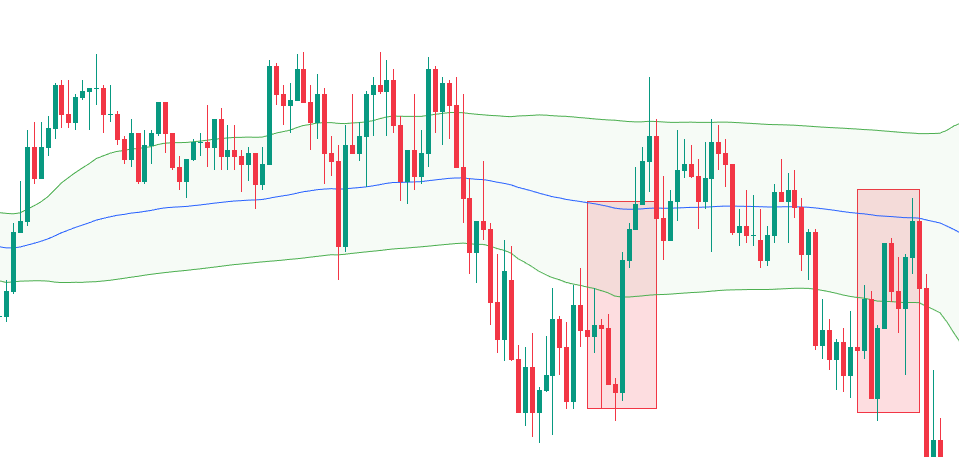
b) VWAP as Dynamic Support and Resistance
VWAP frequently behaves like a moving support or resistance level. Unlike static horizontal levels, VWAP adjusts dynamically as volume and price evolve throughout the session.
In trending markets:
- VWAP often acts as support in uptrends
- VWAP often acts as resistance in downtrends
Traders may look for confirmation from price action, such as rejection wicks or continuation patterns, when price interacts with VWAP.
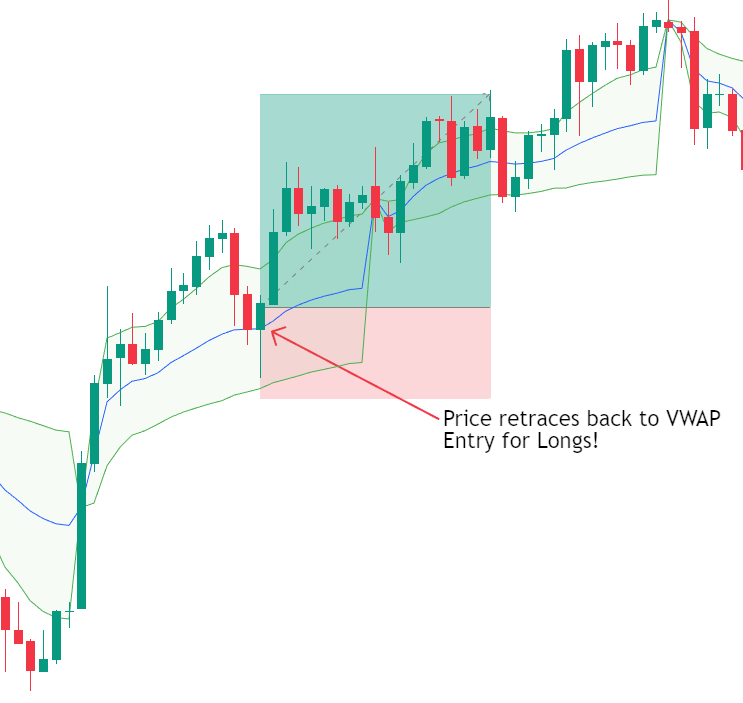
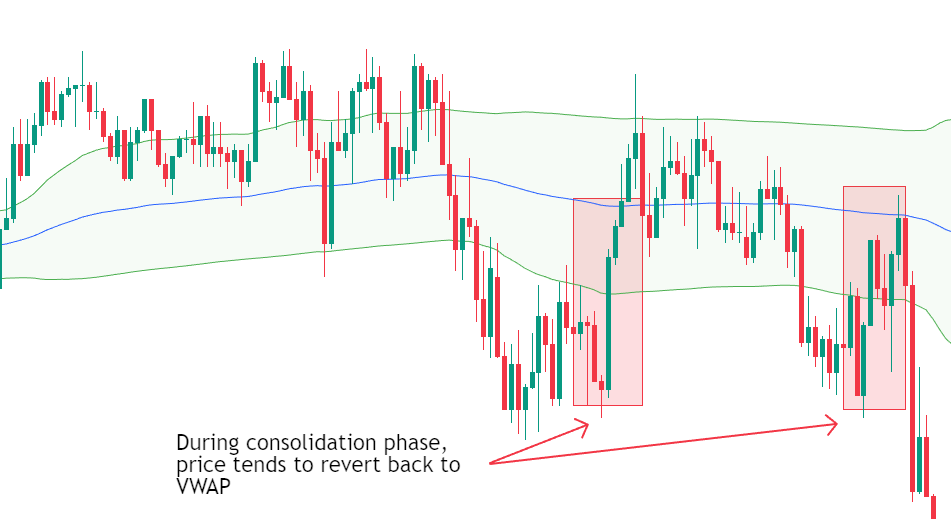
c) VWAP Mean Reversion Strategies
Mean reversion strategies assume that price will revert back towards VWAP after becoming overstretched.
This approach is commonly used when:
- The market lacks strong directional momentum
- Price deviates significantly from VWAP
- Volume begins to decline after an impulsive move
However, mean reversion should be avoided during strong trending sessions, where prices may remain extended for prolonged periods.
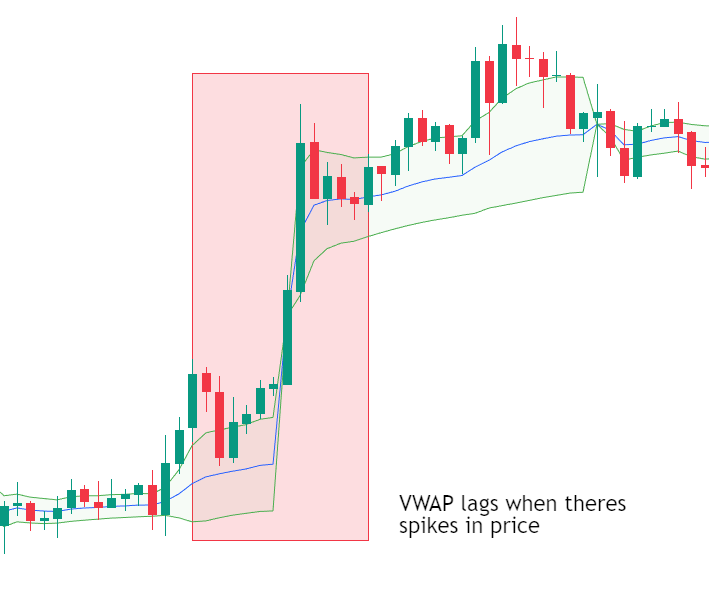
Limitations of VWAP
Despite its strengths, VWAP has limitations:
- It is an intraday indicator and does not provide long-term trend direction
- It can lag during periods of extreme volatility
- It may be less effective in illiquid markets
- It should not be used as a standalone trading system
VWAP works best when combined with price action analysis, market structure, and proper risk management.
Best Practices for Intermediate Traders
Rather than treating VWAP as a standalone indicator, intermediate traders should apply it within a broader market context. The table below outlines key best practices and explains why each one is important.
| Practice | Key Idea |
| Identify Market Conditions | Use VWAP pullbacks in trends and mean reversion in range-bound markets. |
| Align with Higher-Timeframe Bias | Trade in the direction of the dominant higher-timeframe trend. |
| Focus on Volume | VWAP signals are more reliable during high-liquidity sessions such as London and New York. |
| Use Confirmation | Combine VWAP with price action, RSI, MACD, or candlestick patterns. |
Conclusion
VWAP is a sophisticated yet practical tool that offers traders a deeper understanding of intraday market behaviour.
By incorporating both price and volume, VWAP provides insight into fair value, institutional participation, and market sentiment.
For intermediate traders, mastering VWAP is less about memorising strategies and more about understanding context.
When used alongside sound market structure analysis and disciplined risk management, VWAP can significantly enhance trade execution and decision-making.









