
The forex market is a living, breathing ecosystem that is constantly in motion. It never truly stands still. Prices are either moving upward in what’s known as a bullish phase or downward in a bearish phase. Learning to recognize these shifts is one of the most important skills to build confidence and consistency for new traders. VT Markets makes these transitions simple and practical so you can trade with clarity rather than confusion.
But what do the terms “bullish” and “bearish” really mean? How can you identify when a market that’s been falling suddenly starts to rise again? Let’s break it down step by step.
What is a Bearish Market?

A bearish market refers to a period when prices are falling and overall trader sentiment is pessimistic. In forex, this means that one currency is weakening against another, and traders expect this trend to continue. As confidence drops, more people start selling rather than buying, which accelerates the decline.
A bearish phase often develops when traders lose faith in the economy or in a particular currency. Poor economic data, high inflation, rising unemployment, or global political instability can all trigger bearish momentum. The selling pressure feeds on itself: “ the more traders sell, the faster prices fall”.This can lead to what many call a “market crash” in severe cases.
For instance, if the U.S. economy weakens and interest rates drop, the USD might decline against other currencies like the EUR or JPY. This is a clear sign of a bearish trend in the dollar.
Traders face a tough choice during tough times: remain in the market and take the risk, or wait for signs of stability. Some traders attempt to profit by “selling high and buying low,” following the downward trend cautiously. Others prefer to step aside and wait for the dust to settle. Understanding that bearish markets are natural cycles helps traders stay calm and avoid emotional decisions.
What is a Bullish Market?

A bullish market represents optimism and upward momentum. As prices rise steadily, confidence returns, and traders start buying more, pushing prices higher. Bullish phases often follow bearish ones, marking a recovery or renewed strength in the economy or a specific currency.
Positive developments such as strong GDP numbers, declining inflation, stable politics, or encouraging global trade data can all trigger bullish sentiment. When this happens, traders anticipate growth and begin positioning themselves for potential gains.
In forex, this could look like investors buying the EUR/USD pair because they expect the euro to strengthen. As more traders join in, the buying pressure pushes the price higher, a clear sign of a bullish market in motion.
However, even in a bull market, caution is essential. Prices can retrace, corrections can occur, and overconfidence can lead to impulsive trading. The best traders are those who balance optimism with awareness and risk management.
Bullish vs Bearish: Across Forex and Stocks

The terms “bullish” and “bearish” are not limited to forex; they apply across all financial markets, including stocks and commodities. The meaning remains consistent: “bullish” means rising prices, and “bearish” means falling prices. The only difference is the underlying asset.
In forex, you’re observing currency pairs, for example, the euro against the U.S. dollar (EUR/USD). In stocks, you’re watching the price movements of individual companies or indices. Regardless of the asset, recognizing the mood of the market, “the collective optimism or fear,” is what separates informed traders from reactive ones.
When you understand whether the market is bullish or bearish, you can align your trading strategy accordingly, deciding whether to hold, enter, or exit trades at the right time.
When Does a Bearish Market Become Bullish?

The shift from bearish to bullish is often slow and subtle, marked by a change in tone, behavior, and momentum.
At first, the rapid price decline begins to ease. The market stops setting new lows and starts moving sideways. This stabilization is the earliest sign that sellers are losing control. Soon after, small upward movements appear: short rallies that show buyers are slowly returning.
Positive news or data releases can reinforce this recovery. For example, improved employment figures, easing inflation, or a stronger GDP report may spark renewed optimism. Traders begin to believe the worst is behind them, and confidence gradually returns to the market.
As more traders begin buying rather than selling, trading volumes rise. The narrative shifts conversations about “market crashes” into discussions about “recovery” or a possible “bull market.” Finally, the price may break above a key resistance level or trendline, confirming that the bulls are now in control.
It’s important to note that this transition doesn’t happen all at once. The process can take weeks or even months. But for those who are alert and observant, early signals can help you prepare before the next uptrend fully unfolds.
Spotting the Shift Early
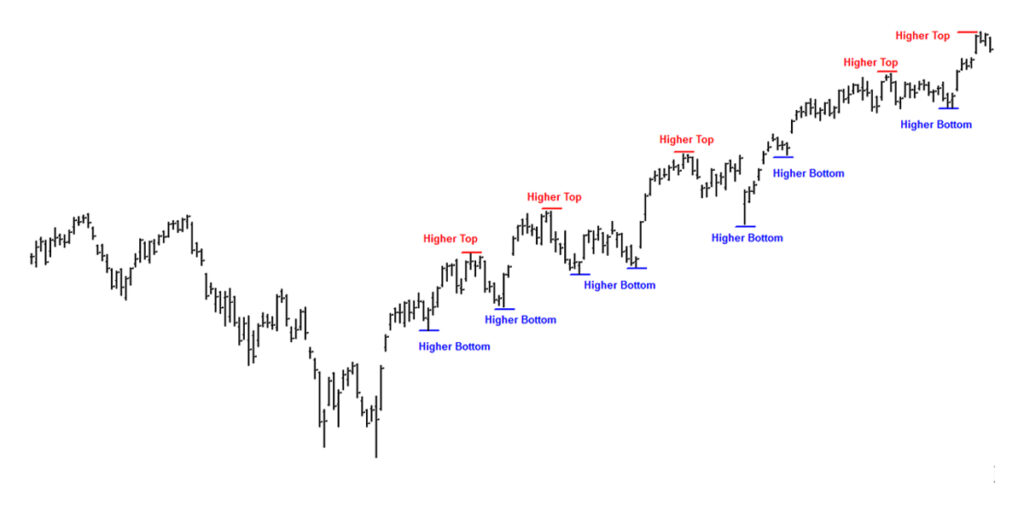
Spotting when a bearish market turns bullish requires observation, patience, and a bit of practice. You don’t need to be an expert analyst to see the signs; you just need to know what to look for.
When prices stop falling and start moving sideways, it’s often the market’s way of catching its breath. If it then breaks above a resistance level, a point where it previously struggled to climb, this may be the first confirmation that buying pressure is increasing.
At the same time, if you notice that economic reports or political developments begin to improve, confidence will usually follow. You might also see a rise in trading activity or volume , an indication that more traders are entering the market, betting on a recovery.
Another key factor is sentiment. Listen to the tone of discussions online or in the news. When fear begins to fade and talk of “hope” or “stability” emerges, that’s often the psychological start of a bullish phase.
By combining these observations: technical patterns, market volume, economic context, and sentiment, traders can gain early insight into where the market is heading next.
How to Trade During Market Transitions
Trading during these transition periods requires both skill and discipline. Patience is your best ally. Wait for clear confirmation before entering a trade. A strong move above resistance or a consistent upward trend across multiple days or weeks provides better reliability than guessing at the first sign of a bounce.
Risk management remains crucial. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and only risk a small portion of your capital on any single trade. Avoid chasing rallies impulsively; instead, wait for pullbacks or retests to enter with a better price.
Traders should also pay attention to global macroeconomic events. Major data releases like inflation figures, GDP reports, or central bank statements can either accelerate or reverse trends quickly. Understanding these dynamics allows you to adjust strategies before the market reacts dramatically.
Conclusion
Every trader experiences both bullish and bearish markets! They are part of the natural rhythm of forex. What separates successful traders from the rest is not luck but awareness. Recognizing the early signs of change, staying composed during volatility, and acting based on strategy rather than emotion are what build long-term success.

At VT Markets, we simplify the complexity of market behavior so even beginners can understand it clearly. Whether the market is roaring like a bull or retreating like a bear, we help you learn how to stay balanced, informed, and confident.







